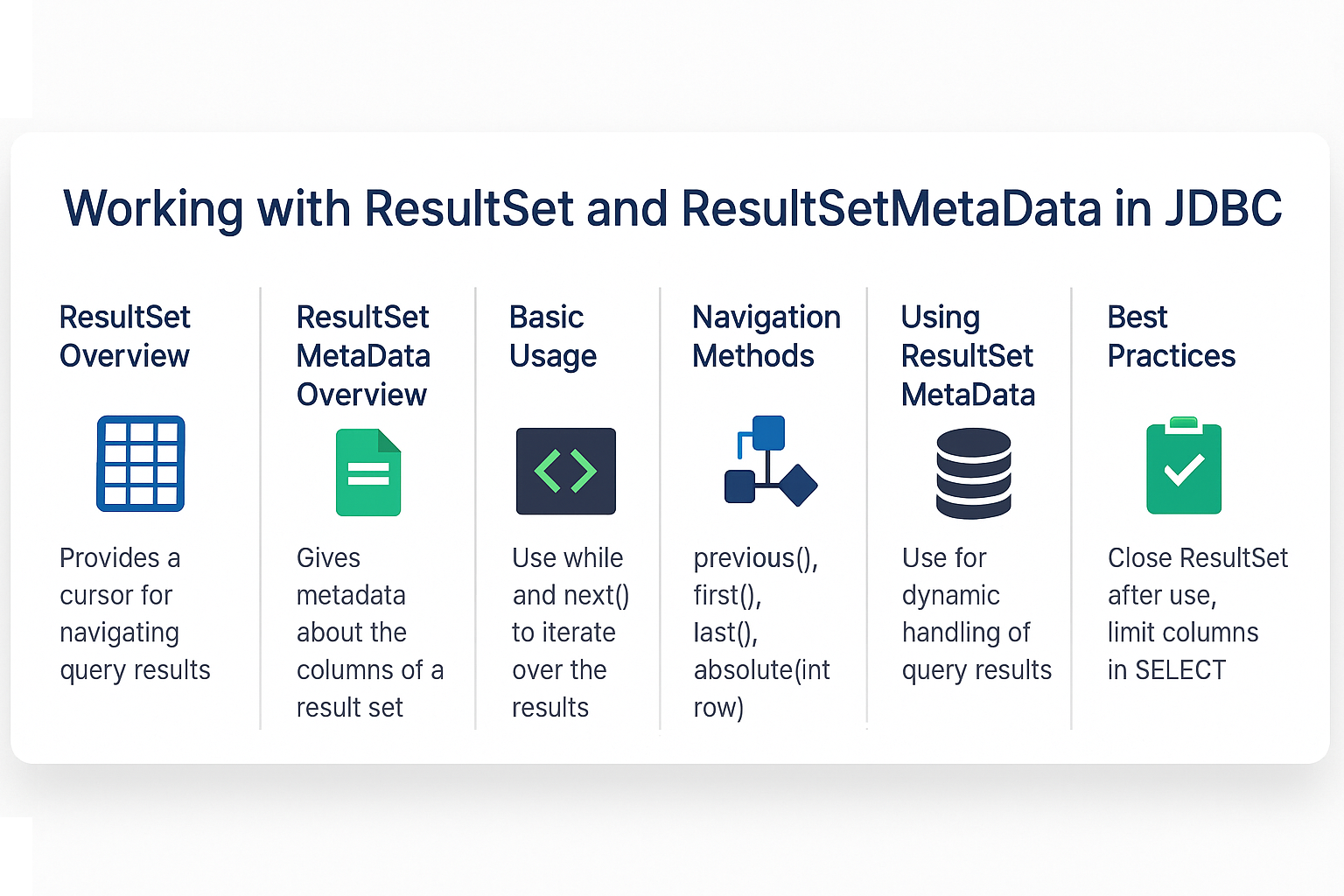
Introduction
When working with JDBC in Java, fetching and handling query results is as important as executing the queries. ResultSet and ResultSetMetaData are two key interfaces that allow developers to read database query results and understand the structure of the result set dynamically.
Why ResultSet and ResultSetMetaData Matter
- Data Retrieval:
ResultSetprovides a cursor to navigate through query results. - Dynamic Metadata:
ResultSetMetaDatagives column information at runtime, making applications more flexible. - Foundation for ORM Frameworks: Hibernate and JPA rely on these concepts internally.
Core Concepts
What is ResultSet?
ResultSet is an interface in JDBC used to store the result of a SELECT query. It acts like a cursor, allowing you to iterate through rows and retrieve column values.
What is ResultSetMetaData?
ResultSetMetaData provides information about the columns in a ResultSet, such as name, type, and count, enabling dynamic query handling.
ResultSet Workflow
Java App → Statement/PreparedStatement → SQL Query → Database → ResultSet → Processing
Real-World Use Cases
- Dynamic Reporting: Display table data without knowing columns at compile time.
- Data Migration: Exporting database content to CSV/Excel.
- Generic Database Tools: Building SQL query analyzers or admin panels.
Working with ResultSet
Basic Example
import java.sql.*;
public class ResultSetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb";
String user = "root";
String password = "password";
String query = "SELECT id, name, role FROM employees";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(query)) {
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String role = rs.getString("role");
System.out.println(id + " | " + name + " | " + role);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Navigating ResultSet
next(): Moves to next row.previous(): Moves to previous row (for scrollable ResultSet).first(),last(): Move to first/last row.absolute(int row): Moves to a specific row.
Using ResultSetMetaData
Example: Displaying Column Names Dynamically
String query = "SELECT * FROM employees";
try (ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(query)) {
ResultSetMetaData meta = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = meta.getColumnCount();
// Print column names
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
System.out.print(meta.getColumnName(i) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
// Print rows
while (rs.next()) {
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
System.out.print(rs.getString(i) + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Statement vs PreparedStatement for ResultSet
| Feature | Statement | PreparedStatement |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection Safety | Vulnerable | Safe with parameter binding |
| Dynamic Query Support | Hardcoded SQL | Parameterized queries |
| Performance | Re-parsed each time | Precompiled, faster on reuse |
Common Mistakes and Anti-Patterns
- Not closing ResultSet: Leads to memory and resource leaks.
- Hardcoding column indexes: Use column names or metadata for flexibility.
- Assuming ResultSet is always scrollable: By default, it's forward-only.
- Mixing business logic and SQL processing: Keep concerns separate.
Security Implications
- Always use
PreparedStatementto prevent SQL injection. - Validate user input even when using parameterized queries.
- Limit database privileges to minimize risks.
Performance and Scalability
- Use only required columns in SELECT to reduce ResultSet size.
- Use streaming for large data sets to avoid memory issues.
- Close ResultSet as soon as processing is done.
Best Practices
- Use try-with-resources to auto-close ResultSet and Statement.
- Rely on
ResultSetMetaDatafor dynamic queries. - Use connection pooling for better resource management.
- Avoid SELECT *; specify required columns for efficiency.
Real-World Analogy
Think of ResultSet as a spreadsheet cursor that lets you move row by row, while ResultSetMetaData is like the header row that tells you the structure of the spreadsheet.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
ResultSetretrieves and navigates query results.ResultSetMetaDataprovides runtime metadata for dynamic queries.- Always close resources and use best practices for performance and security.
FAQ
-
What is ResultSet in JDBC?
It stores the results of a SQL SELECT query in a tabular format. -
What is ResultSetMetaData used for?
To get information about columns such as names, types, and count at runtime. -
Is ResultSet scrollable by default?
No, it's forward-only unless you create a scrollable type. -
Can I update data using ResultSet?
Yes, if you create an updatable ResultSet with the right options. -
What is the difference between column index and column name in ResultSet?
Indexes start from 1; names refer to actual column names. -
Does ResultSet work with all databases?
Yes, as long as the JDBC driver supports it. -
How to handle large ResultSets?
Use pagination, streaming, and avoid loading all data into memory. -
Is closing ResultSet mandatory?
Yes, always close it to free resources. -
What is the benefit of ResultSetMetaData?
Enables dynamic, database-agnostic applications. -
Can ResultSet be used with PreparedStatement?
Yes, and it's recommended for secure and parameterized queries.