Introduction
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is the traditional way to access databases in Java. However, as applications grow, maintaining raw SQL and boilerplate code becomes challenging. JPA (Java Persistence API) and Spring Data abstract database operations, providing a more declarative and maintainable approach.
Why Migrate from JDBC to JPA and Spring Data?
- Reduce Boilerplate: JPA handles SQL generation and object mapping.
- Maintainability: Easier to manage large codebases with entity classes.
- Portability: Works across multiple databases without changing code.
- Integration: Spring Data provides repository patterns and built-in CRUD methods.
Core Concepts
JDBC
- Direct SQL execution with manual result mapping.
- Requires explicit connection management.
JPA
- Object-relational mapping (ORM) standard in Java.
- Maps Java classes to database tables.
Spring Data JPA
- Builds on top of JPA.
- Provides repository abstraction and query generation.
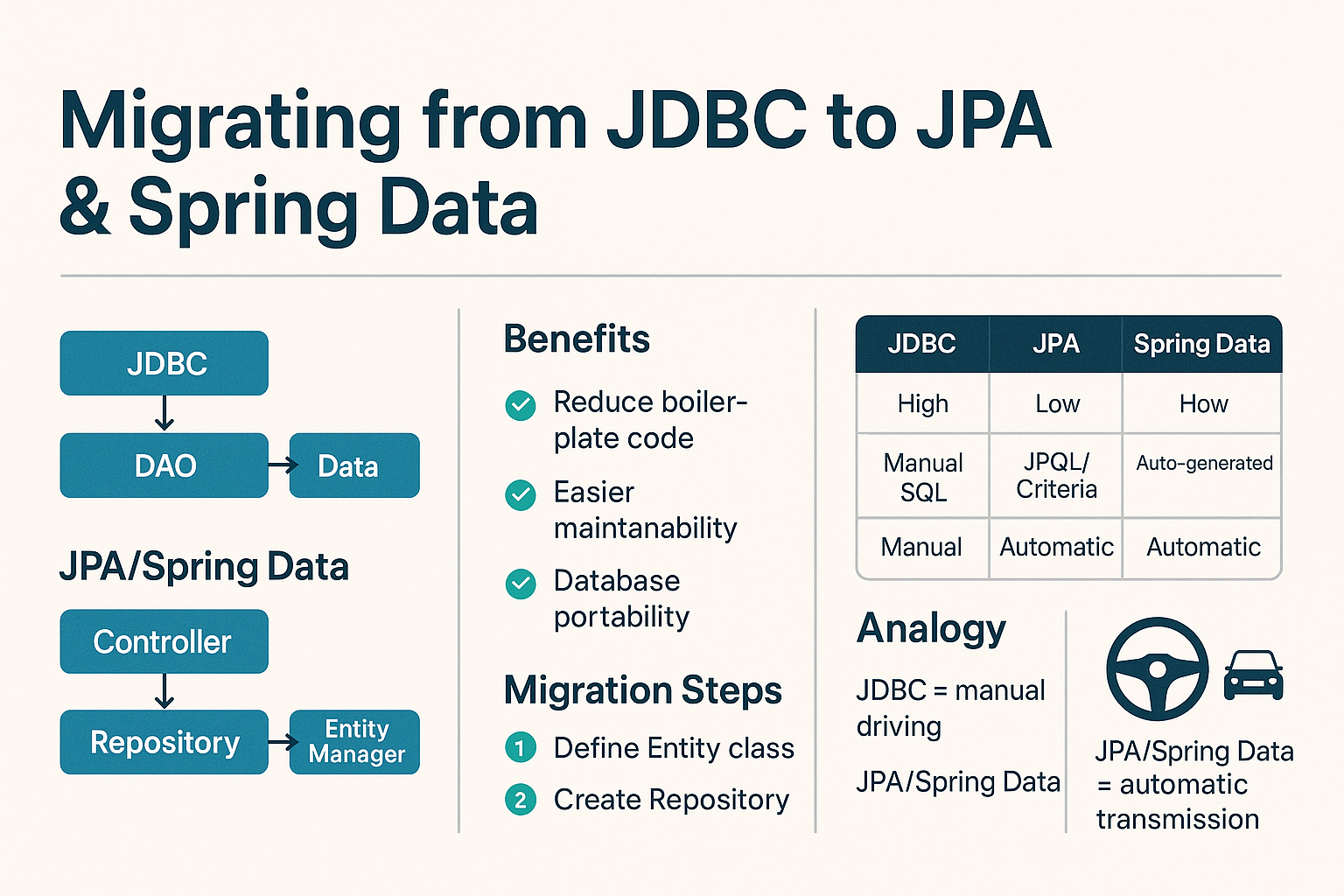
Architecture Comparison
JDBC: Controller → DAO (SQL + JDBC) → Database
JPA/Spring Data: Controller → Repository (JPA) → Entity Manager → Database
Real-World Use Cases
- Enterprise Applications: Migrate legacy JDBC code to scalable Spring Boot apps.
- Microservices: Use Spring Data for modular, maintainable services.
- E-commerce Platforms: Simplify complex relationships between entities.
Migrating from JDBC to JPA
Step 1: Define Entity Class
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String role;
// Getters and setters
}
Step 2: Create Repository Interface
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> {
List<Employee> findByRole(String role);
}
Step 3: Replace DAO with Repository
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository repo;
public void addEmployee(Employee emp) {
repo.save(emp);
}
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
return repo.findAll();
}
}
JDBC vs JPA vs Spring Data
| Feature | JDBC | JPA | Spring Data JPA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boilerplate Code | High | Medium | Low |
| Query Writing | Manual SQL | JPQL/Criteria | Auto-generated queries |
| Object Mapping | Manual | Automatic (ORM) | Automatic (ORM + Repositories) |
| Performance | High (low-level) | Slight overhead (ORM) | Similar to JPA |
| Learning Curve | Low | Medium | Medium |
Common Mistakes During Migration
- Not optimizing queries: ORM can generate inefficient SQL.
- Ignoring lazy loading: Leads to N+1 query problems.
- Mixing JDBC and JPA improperly: Causes transaction issues.
- Skipping entity design: Poor entity relationships hurt performance.
Security Implications
- JPA and Spring Data use parameter binding, preventing SQL injection.
- Use proper transaction isolation to avoid dirty reads.
- Limit repository exposure in public APIs.
Performance and Scalability
- Use
@Queryor native queries for complex, optimized SQL. - Enable second-level caching for frequently accessed entities.
- Profile generated SQL using tools like Hibernate Statistics.
Best Practices
- Start migration module by module, not all at once.
- Map entities carefully with proper annotations.
- Use repositories for CRUD; custom queries only when needed.
- Keep transactions short and consistent.
Real-World Analogy
Think of JDBC as manual driving – you have full control but need to manage everything. JPA and Spring Data are like automatic transmission cars – they handle the complex shifting, letting you focus on the road (business logic).
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
- Migrating to JPA and Spring Data simplifies database access.
- JPA reduces boilerplate, and Spring Data accelerates development.
- Plan migration carefully with performance and security in mind.
FAQ
-
Is JPA faster than JDBC?
JDBC is lower-level and can be faster; JPA trades some speed for maintainability. -
Can I use JDBC and JPA together?
Yes, you can mix them in the same application with proper transaction management. -
What is the role of Hibernate in JPA?
Hibernate is the most popular JPA implementation. -
Does Spring Data replace DAO?
Yes, repositories act as DAO layers with built-in CRUD. -
Can JPA work without Spring?
Yes, JPA is a Java EE standard independent of Spring. -
How to handle custom queries in Spring Data?
Use@Queryannotations or define methods following naming conventions. -
Does JPA prevent SQL injection?
Yes, by using parameterized queries and JPQL. -
Is migration from JDBC to JPA hard?
It requires planning but reduces long-term maintenance costs. -
Does JPA support multiple databases?
Yes, with proper configuration and drivers. -
Should I migrate all JDBC code at once?
No, migrate gradually to reduce risk.