Introduction
The DAO (Data Access Object) Pattern is a design pattern used to separate database interaction logic from business logic. When combined with JDBC, it helps create clean, maintainable, and testable code for database-driven applications.
Why DAO Pattern with JDBC Matters
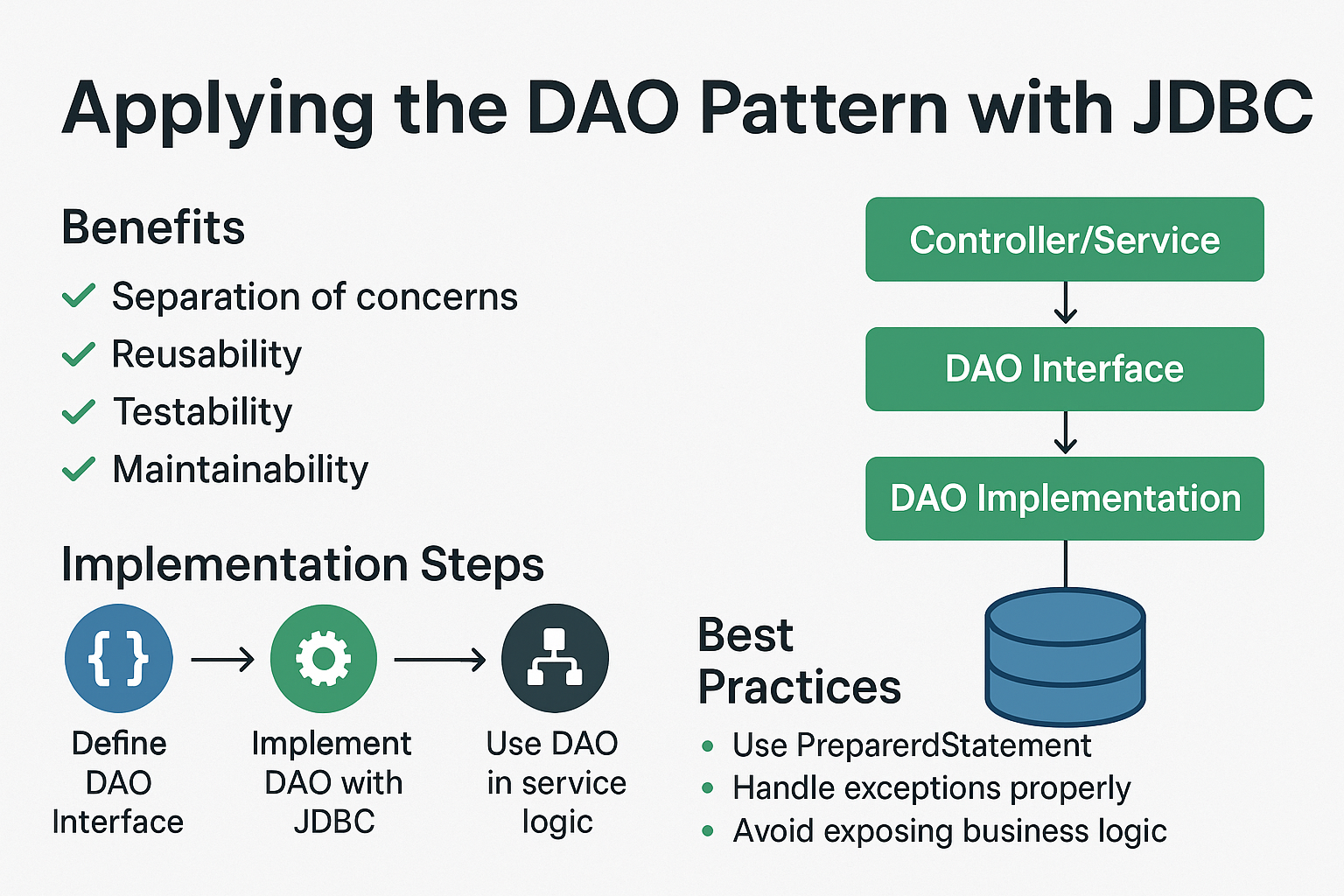
- Separation of Concerns: Keeps data access code separate from application logic.
- Reusability: Centralizes database operations for reuse across the application.
- Testability: Makes unit testing easier with mockable DAO layers.
- Maintainability: Reduces code duplication and simplifies maintenance.
Core Concepts of DAO Pattern
- DAO Interface: Defines CRUD operations.
- DAO Implementation: Implements the interface using JDBC.
- Model/Entity Class: Represents the database table.
- Service Layer: Calls DAO methods without worrying about JDBC code.
DAO Architecture
Controller/Service → DAO Interface → DAO Implementation (JDBC) → Database
Real-World Use Cases
- Enterprise Applications: CRM, ERP, and banking systems.
- Web Applications: E-commerce platforms with complex data models.
- Microservices: Isolating data access in service-based architectures.
Implementing DAO Pattern with JDBC
Step 1: Create the Model Class
public class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
private String role;
// Constructors, getters, and setters
}
Step 2: Create the DAO Interface
import java.util.List;
public interface EmployeeDAO {
void addEmployee(Employee emp);
Employee getEmployeeById(int id);
List<Employee> getAllEmployees();
void updateEmployee(Employee emp);
void deleteEmployee(int id);
}
Step 3: DAO Implementation Using JDBC
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
public class EmployeeDAOImpl implements EmployeeDAO {
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb";
private static final String USER = "root";
private static final String PASSWORD = "password";
@Override
public void addEmployee(Employee emp) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees (name, role) VALUES (?, ?)";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
ps.setString(1, emp.getName());
ps.setString(2, emp.getRole());
ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Employee getEmployeeById(int id) {
String sql = "SELECT id, name, role FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
ps.setInt(1, id);
try (ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery()) {
if (rs.next()) {
return new Employee(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("name"), rs.getString("role"));
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>();
String sql = "SELECT id, name, role FROM employees";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
list.add(new Employee(rs.getInt("id"), rs.getString("name"), rs.getString("role")));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
@Override
public void updateEmployee(Employee emp) {
String sql = "UPDATE employees SET name=?, role=? WHERE id=?";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
ps.setString(1, emp.getName());
ps.setString(2, emp.getRole());
ps.setInt(3, emp.getId());
ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void deleteEmployee(int id) {
String sql = "DELETE FROM employees WHERE id=?";
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
ps.setInt(1, id);
ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Step 4: Using the DAO in Application
public class EmployeeService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EmployeeDAO dao = new EmployeeDAOImpl();
dao.addEmployee(new Employee(0, "Alice", "Developer"));
Employee emp = dao.getEmployeeById(1);
System.out.println(emp.getName() + " - " + emp.getRole());
}
}
Statement vs PreparedStatement in DAO
| Feature | Statement | PreparedStatement |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection Safety | Vulnerable | Safe with parameter binding |
| Performance | Re-parsed each execution | Precompiled, faster on reuse |
| Maintenance | Harder to manage | Easier and cleaner |
Common Mistakes and Anti-Patterns
- Mixing DAO and Business Logic: Violates separation of concerns.
- Not using PreparedStatement: Leads to SQL injection risks.
- Hardcoding DB credentials: Use configuration files or environment variables.
- Not handling exceptions properly: Leads to unstable applications.
Security Implications
- Always use parameterized queries to avoid SQL injection.
- Use least privilege DB accounts for DAOs.
- Secure sensitive information like DB credentials.
Performance and Scalability
- Use connection pooling to avoid frequent connection creation.
- Cache frequently accessed data when appropriate.
- Keep DAOs stateless for thread safety.
Best Practices
- Keep DAO methods focused and simple.
- Use interfaces for flexibility and testability.
- Use PreparedStatement for all dynamic queries.
- Combine with connection pooling for production systems.
Real-World Analogy
Think of the DAO pattern as a translator between your application and the database. The service layer speaks in business terms, while the DAO translates it into SQL language for the database to understand.
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
- DAO pattern separates data access logic from business logic.
- Combine DAO with JDBC for clean, maintainable code.
- Use PreparedStatements and pooling for secure, performant DAOs.
FAQ
-
What is DAO pattern in Java?
A design pattern that abstracts and encapsulates all access to the data source. -
Why use DAO with JDBC?
To separate database logic from business logic and improve maintainability. -
Can DAO be used with different databases?
Yes, by changing the JDBC implementation details. -
Is DAO only for relational databases?
No, it can be adapted for NoSQL databases as well. -
How to test DAO classes?
Use mock databases or in-memory databases like H2. -
Does DAO pattern improve performance?
Indirectly, by promoting pooling and clean design. -
Should DAO handle transactions?
Basic transaction handling can be in DAO; complex ones in service layer. -
What is the difference between DAO and Repository pattern?
DAO focuses on data access; Repository is domain-driven with aggregation logic. -
Can DAO be used with ORM frameworks?
Yes, though ORMs often abstract DAOs internally. -
Is DAO pattern still relevant in modern Java?
Absolutely; it's widely used in enterprise and legacy applications.