Selecting the proper data type is the first step to writing efficient, bug‑free Java code. The data type tells the compiler how much memory to allocate and what operations are legal.
1️⃣ Primitive Data Types
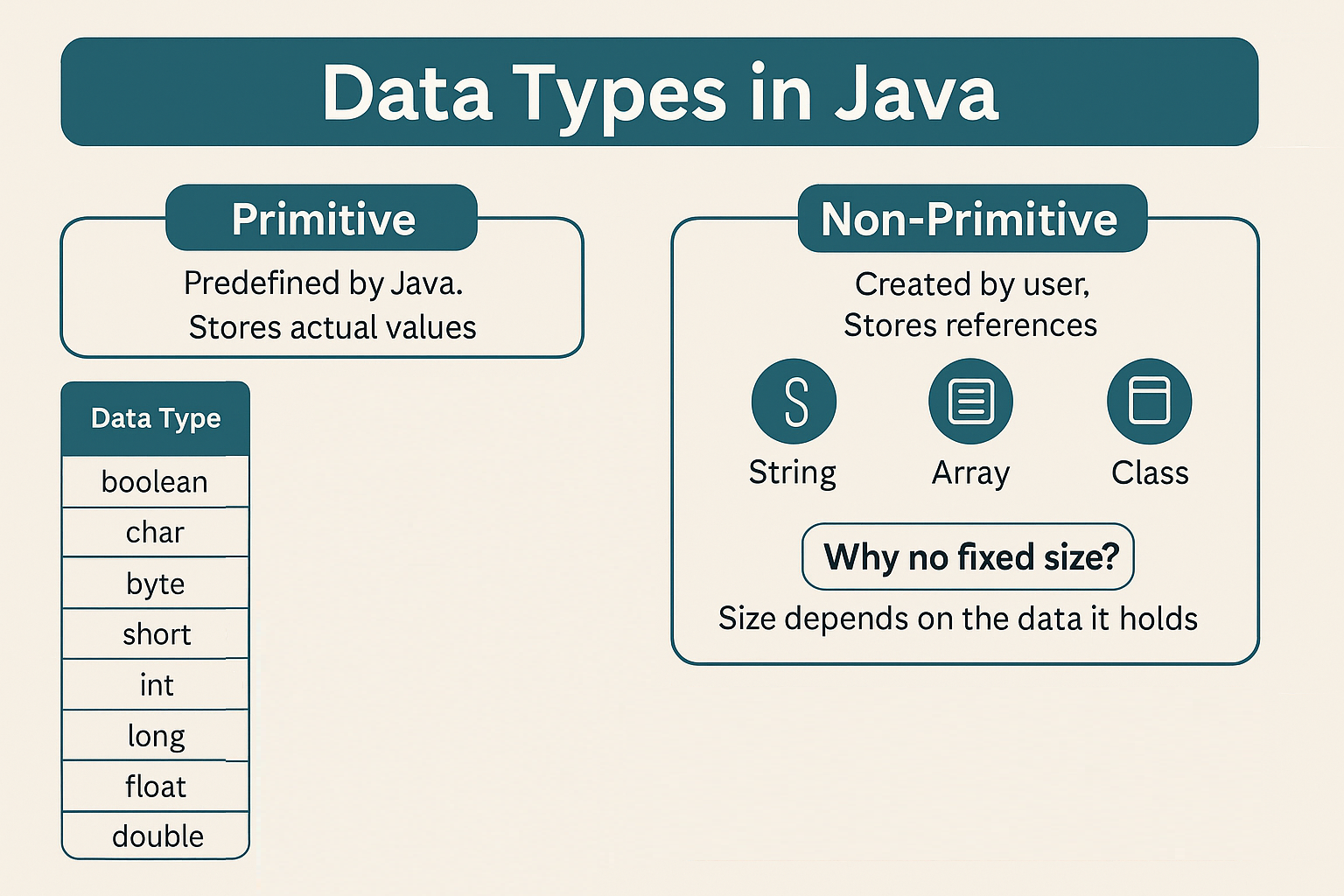
Primitive types are built into the JVM and store actual values in stack memory. They have fixed size and no additional methods.
| Type | Size (bits) | Default | Min Value | Max Value | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
boolean |
JVM‑specific | false |
false |
true |
Flags, status |
char |
16 | \u0000 |
\u0000 |
\uFFFF |
Single Unicode character |
byte |
8 | 0 |
‑128 |
127 |
I/O streams, raw data |
short |
16 | 0 |
‑32 768 |
32 767 |
Memory‑critical arrays |
int |
32 | 0 |
‑2 147 483 648 |
2 147 483 647 |
Default integer |
long |
64 | 0L |
‑2⁶³ |
2⁶³‑1 |
Large counters, timestamps |
float |
32 | 0.0f |
‑3.4E38 |
3.4E38 |
Low‑precision decimals |
double |
64 | 0.0d |
‑1.7E308 |
1.7E308 |
High‑precision decimals |
int age = 30;
double price = 19.99;
boolean isActive = true;
Performance Note
Arithmetic on primitives is hardware‑level—much faster than object wrappers like Integer or Double.
2️⃣ Non‑Primitive (Reference) Data Types
Non‑primitive types store references to objects in heap memory. Size is dynamic and depends on content.
| Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
String |
Sequence of characters (immutable) | "Hello" |
Array |
Ordered collection of primitives/objects | int[] nums = {1,2,3}; |
Class |
Blueprint for objects | class Student { ... } |
| Others | Interface, Enum, Annotation |
Runnable, enum Color |
Why No Fixed Size?
The JVM can’t predict how many elements a user will store in an Array or how many fields a custom Class will contain.
3️⃣ Choosing the Right Type (Real‑World Scenario)
Problem: Store 1 000 000 sensor readings with decimals.
floatsaves memory (4 MB) but risks precision loss.doubledoubles memory (8 MB) but retains accuracy.BigDecimal(non‑primitive) offers arbitrary precision but is 10–20× slower.
Rule of Thumb: Start with
double. Optimize tofloatorBigDecimalonly when profiling proves the need.
4️⃣ Common Mistakes & Anti‑Patterns
| Mistake | Impact | Fix |
|---|---|---|
Using float for currency |
Rounding errors | Use BigDecimal |
Mixing int and double in arithmetic |
Implicit cast may surprise | Cast explicitly |
| Using wrapper types in tight loops | Autoboxing overhead | Stick to primitives |
5️⃣ Interview Nuggets
- Q: Why is
Stringnot a primitive?
A: Because it offers methods and dynamic sizing, implemented as an object. - Q: Difference between
==on primitives vs objects?
A: Primitives compare values; objects compare references unless overridden.
🧭 Version Relevance
| Feature | Java Version | Notes |
|---|---|---|
strictfp keyword |
1.2 | Guarantees FP consistency |
var (local type inference) |
10 | Still infers to a primitive or reference type underneath |
| Records (compact classes) | 16 | Non‑primitive, concise data carriers |
📝 Summary
- Primitives = fixed size, fast, no methods.
- Non‑Primitives = reference types, variable size, rich APIs.
- Right sizing improves performance and memory efficiency.
Next: Build a small program that benchmarks primitive arrays vs
ArrayList<Integer>for 10 million additions.