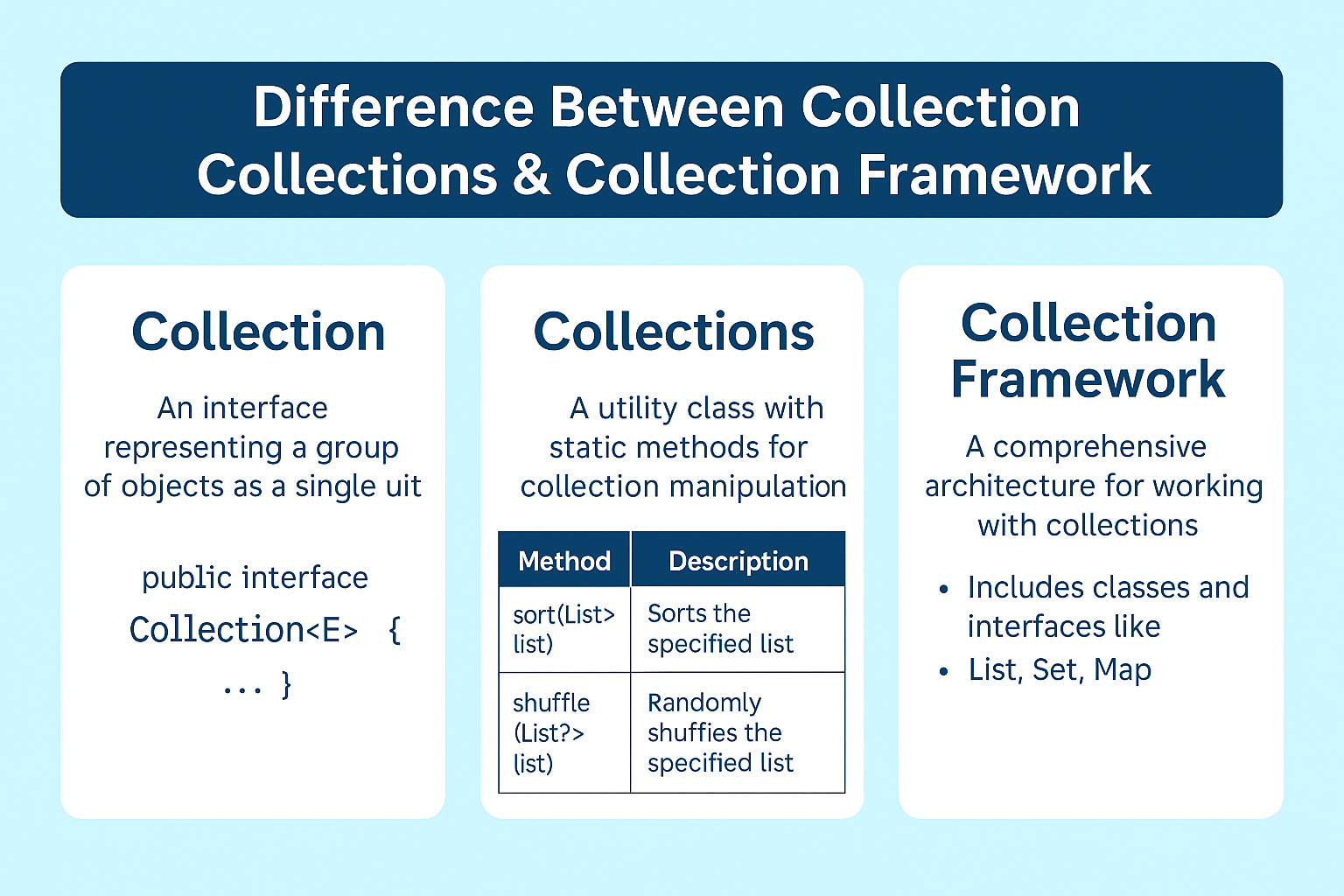
When new Java developers hear “Collection,” “Collections,” and “Collection Framework,” confusion is almost guaranteed. Are they the same? Are they different? This article breaks down each term, shows code in action, and equips you with talking points for interviews.
⚡ Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | Collection (Interface) | Collections (Utility Class) | Collection Framework (Concept) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Root interface in java.util |
Final class in java.util |
Umbrella term (classes + interfaces) |
| Purpose | Defines basic operations for a group of objects | Provides static helper methods (sort, shuffle) | Provides data structures & algorithms |
| Examples | List, Set, Queue extend it |
Collections.sort(list) |
ArrayList, HashMap, TreeSet, etc. |
| Instantiable? | No (interface) | No (all static) | N/A (concept) |
| Since | Java 1.2 | Java 1.2 | Formalised in Java 1.2 |
🔹 1. Collection Interface (java.util.Collection)
The Collection interface is the grandparent of almost every container in Java (except arrays and maps).
// Example: removing duplicates with a Set
Collection<String> names = new HashSet<>();
names.add("Alice");
names.add("Bob");
names.add("Alice"); // duplicate ignored
System.out.println(names); // [Alice, Bob]
Key Points
- Defines size, add, remove, iterator, etc.
List,Set, andQueueare sub‑interfaces.- Cannot be instantiated directly.
When to reference it: When you want maximum flexibility in APIs (
void saveAll(Collection<?> items)).
🔹 2. Collections Class (java.util.Collections)
Collections is a utility class packed with static methods that operate on instances of Collection or its sub‑types.
Frequently Used Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
sort(List<T> list) |
Sort by natural order |
sort(List<T> list, Comparator<T> c) |
Sort by custom comparator |
shuffle(List<?> list) |
Randomly permute list |
reverse(List<?> list) |
Reverse order |
swap(List<?> list, int i, int j) |
Swap two elements |
synchronizedCollection(Collection<T> c) |
Return thread‑safe wrapper |
List<Integer> nums = Arrays.asList(3, 1, 4, 1, 5);
Collections.sort(nums); // [1, 1, 3, 4, 5]
Collections.reverse(nums); // [5, 4, 3, 1, 1]
Collections.shuffle(nums); // Random order
Tip
Need thread safety? Use Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>())—or better, CopyOnWriteArrayList for read‑heavy workloads.
🔹 3. Collection Framework (The Big Picture)
The Java Collection Framework (JCF) is the architecture that bundles:
- Interfaces –
Collection,List,Set,Queue,Map - Implementations –
ArrayList,HashSet,LinkedList,HashMap, etc. - Algorithms – Provided via
CollectionsandArraysutility classes
Diagram (Textual)
+-------------------+
| Collection |
+---------+---------+
| | |
List Set Queue
| | |
ArrayList HashSet ArrayDeque
Why it matters: The framework standardizes data structures so you don’t reinvent the wheel.
🚀 Use‑Cases & Best Practices
| Scenario | Best Choice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Need an ordered, resizable list | ArrayList (implements List → Collection) |
Fast random access |
| Need duplicate‑free set | HashSet (implements Set → Collection) |
O(1) add/contains |
| Need to sort periodically | Collections.sort(list) |
In‑place quicksort/merge |
| Need thread-safe iteration | Collections.synchronizedCollection(coll) or ConcurrentHashMap |
Built‑in wrappers |
🛑 Common Mistakes
- Confusing
CollectionsandCollection. Remember: s for static utilities. - Trying to instantiate
Collectiondirectly. Use an implementation. - Mixing raw and generic types – leads to
ClassCastException.
🎯 Interview Angle
Q: What’s the difference between
Collections.sort()andList.sort()?
A:List.sort()(Java 8) is a default method;Collections.sort()is static. Both delegate to the same TimSort algorithm, butList.sort()can be overridden.
🧭 Java Version Relevance
| Feature | Introduced | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Collection Framework & Collections |
Java 1.2 | Major library overhaul |
| Generics | Java 5 | List<String> |
Diamond operator (<>) |
Java 7 | new ArrayList<>() |
Default methods (List.sort) |
Java 8 | Functional improvements |
Unmodifiable collections (List.of) |
Java 9 | Factory methods |
📝 Summary
- Collection (interface): Contract for containers.
- Collections (class): Utility toolkit for collections.
- Collection Framework: The entire ecosystem of interfaces, classes, and algorithms.
Choose wisely and remember the naming convention: interface singular, class plural.
Next Step: Build a mini student‑management app that stores
Studentobjects in aList, sorts them withCollections.sort, and prints the top performers.